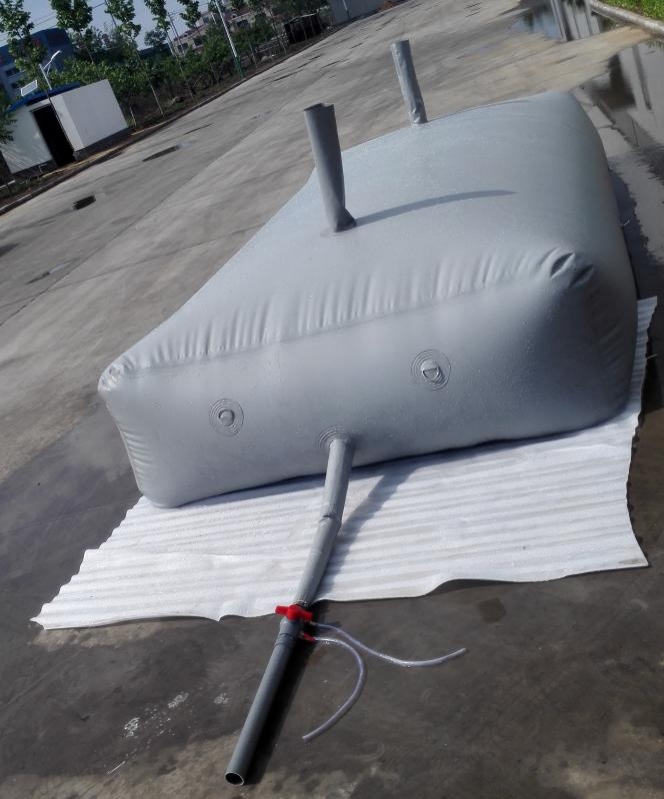
Aquaculture one-stop solution provider & liquid storage equipment manufacturer.
Water Storage Tank Manufacturers Trend Report
Shandong Wolize Biotechnology Co., Ltd. has made a lot of effort in differentiating its water storage tank manufacturers from competitors. Through continually perfecting the materials selection system, only the finest and most appropriate materials are applied to manufacture the product. Our innovative R&D team has made achievement in enhancing the aesthetic appearance and functionality of the product. The product is popular in the global market and believed to have a wider market application in the future.
As a top brand in the industry, WOLIZE plays a crucial role in our company. In the Word-of-Mouth research carried out by the industry association, it attracts people because it is both environmental- and user-friendly. This is also the key reason for the year-by-year increasing sales volume and the stably high repurchase rate. All products under this brand are believed to be of premium quality and excellent performance. They are always in the lead in the market.
We have established solid cooperation with many reliable logistics companies to provide customers with various transportation modes shown at WOLIZE. No matter what kind of transportation mode is chosen, we can promise fast and reliable delivery. We also carefully pack the products in order to make sure they arrive at the destination in good condition.
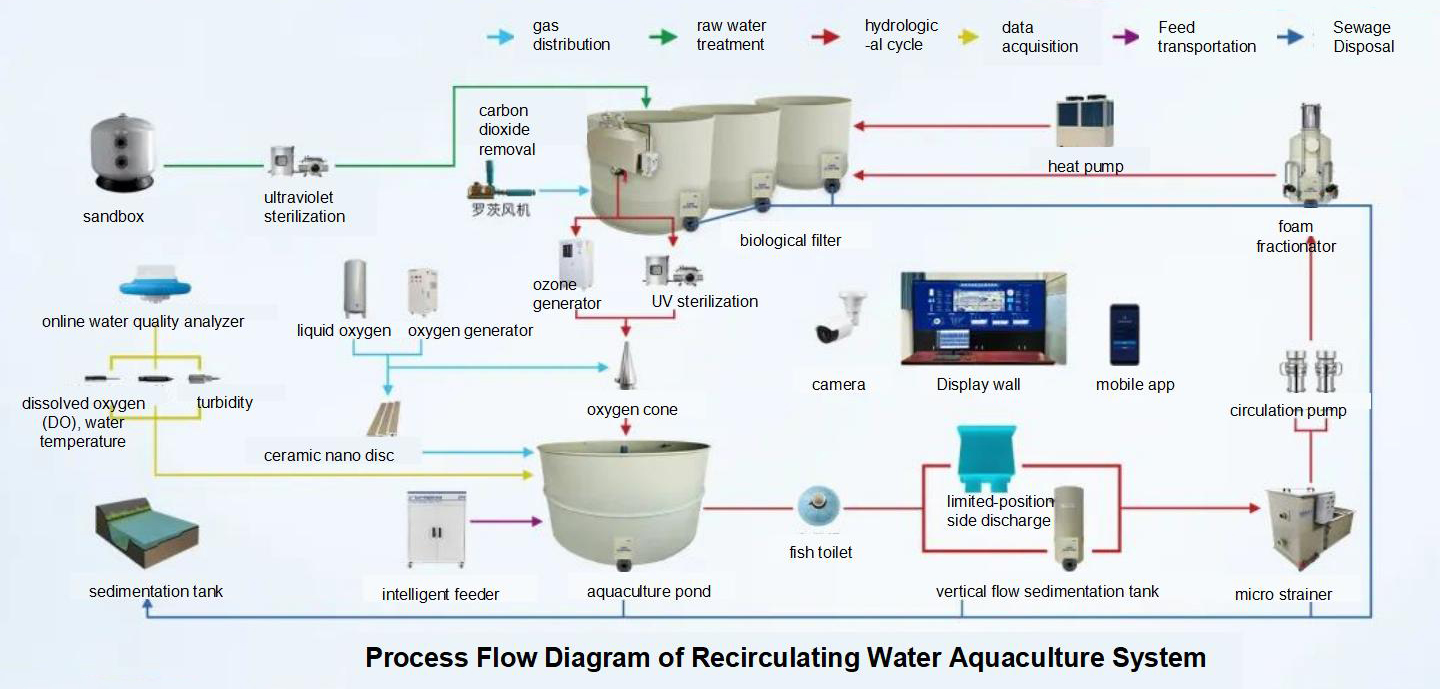
Recirculating Water Quality Parameters
Water quality parameters and design standards form the basis for recirculating water treatment system design and operational management. Below are reference diagrams and parameters commonly used by the Engineering Team:
| Water Quality Parameters | |
Total Suspended Solids (TSS) | ≤10mg/L |
Total Ammonia Nitrogen (TAN) | ≤1mg/L |
Nitrite (NO₂⁻ - N) | ≤0.5mg/L |
Nitrate (NO₃⁻ - N) | ≤300mg/L |
Dissolved Oxygen (DO) | 8-10mg/L |
pH | 7-8.5 |
Oxidation-Reduction Potential (ORP) | ≤400mV |
Water Temperature | 23-30℃ |
1. Solid Particle Removal System Design
Total Suspended Solids (TSS) is commonly used as a parameter to measure solid particulate matter in Recirculating Aquaculture System (RAS). It mainly refers to the total amount of solid particles with a particle size greater than 1 micron in a unit of water. In the circulating water system, TSS includes fish feces, residual bait, biological flocs (dead and live bacteria), etc. The size of these suspended particles varies greatly from micrometer to centimeter level. Suspended particulate matter can directly affect the health and growth of fish (especially cold water fish), and also increase the burden on biofilters. Therefore, it is necessary to maintain the concentration of suspended particles in the circulating water within a reasonable range.
In some EU countries' Recirculating Aquaculture System (RAS) systems, the control of suspended particulate matter is relatively strict. For example, for water bodies used for Recirculating Aquaculture System (RAS), the concentration of suspended particulate matter (measured by total suspended solids TSS) is usually expected to be controlled below 15mg/L to maintain good water quality and ecological environment.
The United States also has relevant water quality regulations in the fields of aquaculture and water treatment. In the Recirculating Aquaculture System (RAS) system, the corresponding suspended particulate matter content (converted by turbidity and other related indicators) also has certain limitations. The ideal range for suspended particulate matter concentration is around 8-12 mg/L, which is used to ensure the survival and reproduction of aquatic organisms.
In the actual operation of the factory based Recirculating Aquaculture System (RAS) system in China, it is generally required to control the suspended particulate matter concentration (suspended solids SS) below 10mg/L. For some precious species that require high water quality, such as salmon, it is even required to control it below 5mg/L.

2. Dissolved Contaminant Removal Parameters
Water solubility includes soluble inorganic substances and soluble organic substances. Among them, water-soluble harmful substances are mainly ammonia nitrogen (NH3-N) and nitrite nitrogen (NO2-- N). Ammonia nitrogen can enter the bloodstream through the gills and skin of fish, disrupting their normal tricarboxylic acid cycle, altering their osmotic pressure, and reducing their ability to absorb oxygen from water, thus affecting their normal growth and survival.
The commonly used fixed membrane nitrification biofilter in Recirculating Aquaculture System (RAS) systems is the ammonia nitrogen conversion bacterial community that grows on the surface of a certain biological packing material, and ammonia nitrogen is transferred to the fixed biofilm through diffusion and converted. The main purpose of the biological filter process design is to ensure that the filter has sufficient nitrifying bacteria to remove ammonia nitrogen excreted by fish, maintain the ammonia nitrogen concentration in the aquaculture system within the predetermined range, and ensure the safety and effective growth of fish.
2.1 Ammonia Nitrogen (NH₃-N) Control
Ammonia nitrogen is one of the main pollutants dissolved in water in Recirculating Aquaculture System (RAS) systems. It mainly comes from the excrement and residual feed of farmed organisms. High concentrations of ammonia nitrogen can be toxic to farmed organisms, affecting their growth, immunity, and reproductive ability. In biofilters, the removal of ammonia nitrogen mainly relies on the nitrification of microorganisms such as nitrifying bacteria, which convert ammonia nitrogen into nitrite and nitrate.
When designing a biofilter, sufficient surface area and volume of the filter material should be considered to provide enough space for nitrifying bacteria to grow and reproduce. At the same time, it is necessary to control the ammonia nitrogen load in the influent and avoid excessive ammonia nitrogen concentration from impacting the biological filter. For example, the concentration of ammonia nitrogen in the influent can be reduced by using an automatic feeding machine and adopting a feeding strategy of small amounts and multiple meals. Determine the allowable ammonia nitrogen concentration for the biofilter based on the ammonia nitrogen tolerance and breeding density of the cultured organisms. Generally speaking, for most freshwater aquaculture fish, the total ammonia nitrogen concentration should be controlled below 1mg/L, and non-ionic ammonia should not exceed 0.025mg/L.
2.2 Nitrite (NO₂⁻-N) Control
Nitrite is also a water quality parameter that needs to be closely monitored in the Recirculating Aquaculture System (RAS) system. It is an intermediate product in the process of ammonia nitrogen nitrification and is also toxic to aquaculture organisms. Nitrite can affect the transport of oxygen in the blood of farmed organisms, leading to symptoms of hypoxia such as shortness of breath, floating heads, and even death.
In the design, it is necessary to ensure that the biofilter can effectively further convert nitrite into nitrate. This requires maintaining the activity of denitrifying bacteria in the biofilter and providing them with suitable environmental conditions, such as appropriate dissolved oxygen. Generally, it is required to control the concentration of nitrite below 0.5mg/L.
2.3 Seawater Aquaculture Considerations
The salinity of seawater is relatively high, containing various ions such as sodium ions (Na ⁺), chloride ions (Cl ⁻), magnesium ions (Mg ² ⁺), calcium ions (Ca ² ⁺), etc. Marine aquaculture organisms have evolved complex ion regulation systems during their long-term adaptation to high salt environments. When nitrite enters marine organisms, these organisms can partially alleviate the physiological effects of nitrite by utilizing their own ion regulation system. In Recirculating Aquaculture System (RAS), chloride ions (Cl -) can reduce the toxicity of nitrite (NO2-) to aquaculture organisms through competitive inhibition. Specifically, both chloride ions and nitrite need to enter the fish body through the chloride cells on the gill plates. The presence of chloride ions increases the difficulty of nitrite entering the fish body, thereby reducing its toxicity. In general, when the concentration of chloride ions in water is six times that of nitrite, it can effectively inhibit the toxicity of nitrite to aquaculture organisms. Compared to freshwater aquaculture, seawater aquaculture has less toxic hazards from nitrite, which is related to the higher concentration of chloride ions in seawater. Therefore, in the Recirculating Aquaculture System (RAS) system, by regulating salinity reasonably, the toxicity of nitrite can be effectively reduced, and the health and safety of aquaculture organisms can be protected.
3. Dissolved Oxygen (DO)
In a Recirculating Aquaculture System (RAS) system, dissolved oxygen (DO) is a key water quality parameter. Fish and other aquatic organisms absorb dissolved oxygen from water through gill respiration to maintain their metabolic activity. The dissolved oxygen concentration required for the normal growth of most warm water fish is generally around 5-8mg/L. When the dissolved oxygen concentration is below the critical level, the respiration of aquatic organisms will be inhibited, their growth rate will slow down, their immunity will decrease, and they are prone to infection with diseases. For example, when the dissolved oxygen is below 2mg/L, many fish will experience floating head phenomenon, and prolonged exposure to low dissolved oxygen can lead to fish death.
In Recirculating Aquaculture System (RAS), it is recommended to maintain dissolved oxygen between 8-10 mg/L. Higher dissolved oxygen is beneficial for increasing feeding levels and reducing feed to feed ratios.
4. pH Control
In a Recirculating Aquaculture System (RAS) system, the suitable pH range for fish is usually between 7.0-8.5. For example, most freshwater fish grow well in environments with pH 7.2-7.8. This is because within this pH range, the physiological functions of fish, such as respiration and osmotic pressure regulation, can be carried out relatively normally. Gas exchange occurs through the gills, and the appropriate acidity or alkalinity in water facilitates the normal exchange process of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
For shrimp farming, such as South American white shrimp, the suitable pH range is roughly 7.8-8.6. This is due to the physiological structure and activity characteristics of crustaceans, which make them more adaptable to slightly higher pH environments. Suitable pH is beneficial for the molting growth of shrimp.
However, during the process of Recirculating Aquaculture System (RAS), the pH value will continuously decrease as the aquaculture progresses, and it is necessary to adjust the pH value of the water. Automatic pH adjustment equipment can be used. Automatically adjust the pH value of the water body based on pH sensor data.
I. Purpose
Water storage liquid bags are widely used in many fields, mainly including:
Agricultural irrigation: In arid areas, liquid bags can store rainwater or irrigation water to help crops grow.
Emergency water storage: In natural disasters or water supply interruptions, liquid bags can be used as emergency water sources.
Outdoor activities: Suitable for outdoor activities such as camping and hiking, easy to carry and use.
Industrial use: In some industrial processes, liquid bags can be used to store and transport liquid raw materials.
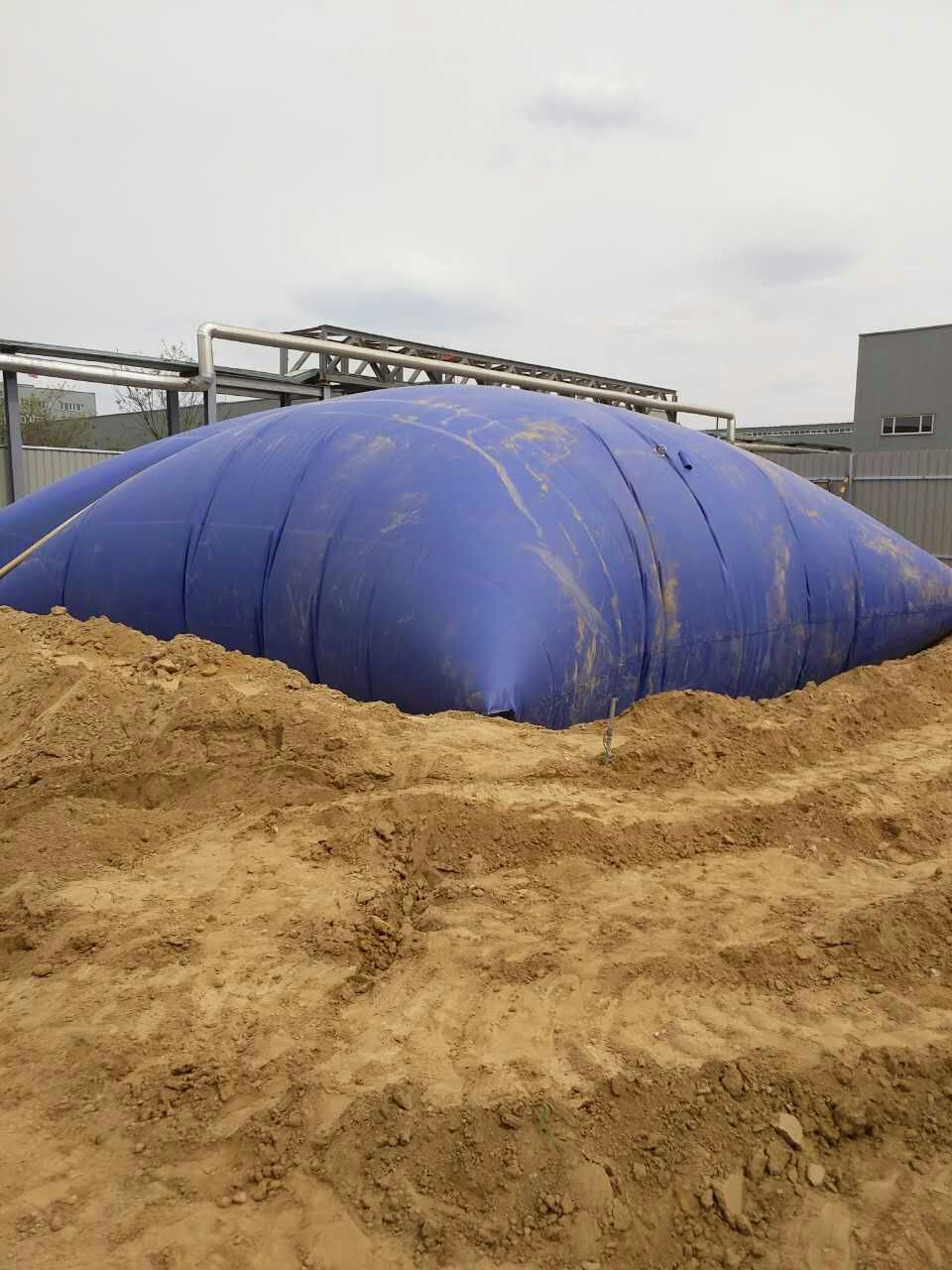

II. Materials
The materials of water storage liquid bags are usually durable and safe, including:
Polyethylene (PE): has good chemical resistance and UV resistance, suitable for long-term outdoor use.
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC): has low cost, but may release harmful substances under high temperature conditions.
TPU (thermoplastic polyurethane): has excellent elasticity and wear resistance, and is often used in high-end products.
Composite materials: Combine the advantages of multiple materials to improve strength and durability.
3. Design
The design of water storage bags is becoming more and more user-friendly and functional, mainly reflected in:
Portability: lightweight design, easy to carry, some products are foldable, saving space.
Versatility: some liquid bags are equipped with a filtration system, and the stored water can be drunk directly.
Durability: enhanced sealing design and wear-resistant materials to extend service life.
Visualization: transparent or translucent material design, easy to observe the amount of water inside.
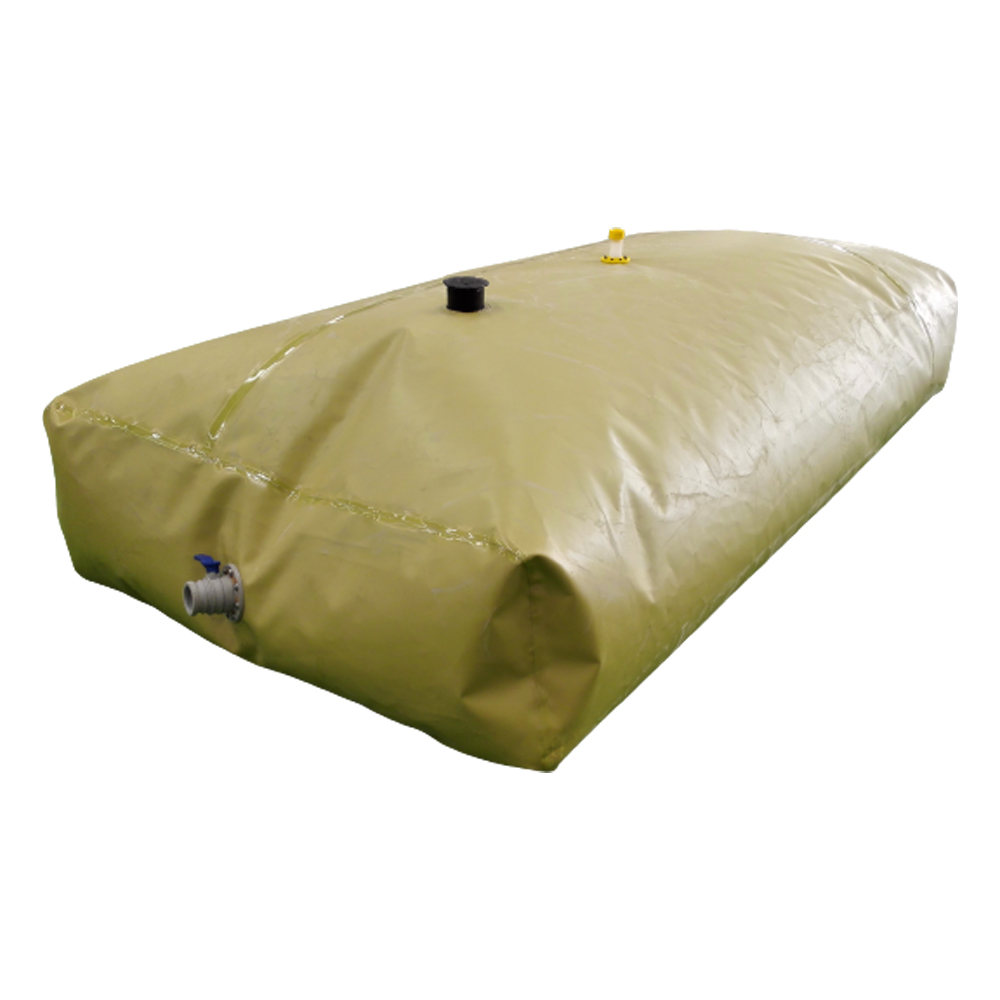

4. Market Trends
The water storage bag market is experiencing rapid development, and the main trends include:
Enhanced environmental awareness: Consumers' attention to environmentally friendly materials and sustainable development has prompted manufacturers to adopt recyclable materials.
Intelligence: Some liquid bags have begun to integrate sensors to monitor water levels and water quality in real time.
Personalized needs: According to different usage scenarios, products with various specifications and functions are launched.
International market expansion: With the intensification of global climate change and water shortage problems, the demand for water storage bags in the international market continues to grow.

Conclusion
Water storage bags play an important role in modern life. Their diverse uses, continuously improving materials and designs, and rapid market development make them an effective tool for addressing water resource challenges. With the advancement of technology and changes in consumer demand, water storage bags in the future will be more intelligent, environmentally friendly and humane.
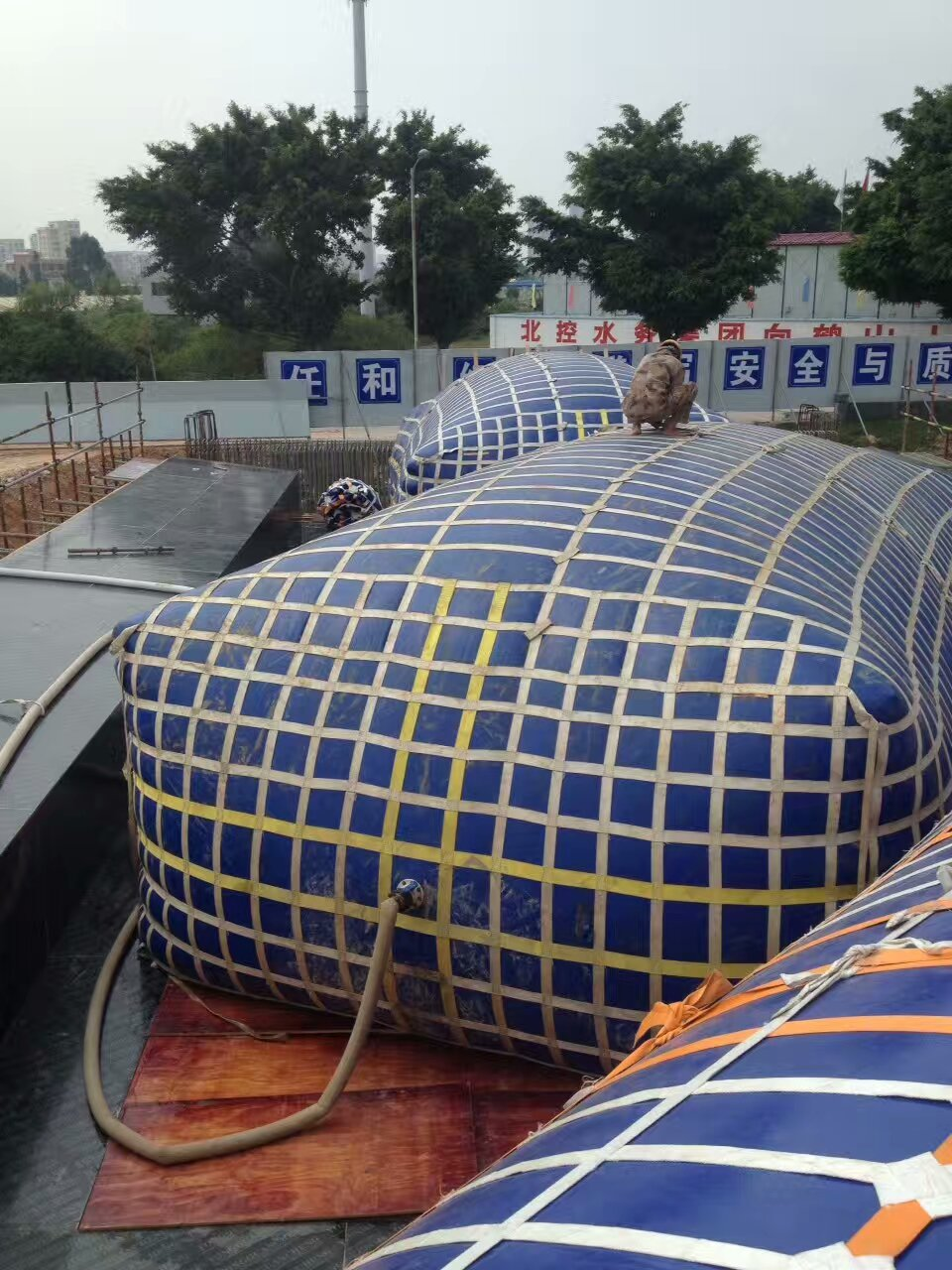
Under severe environmental conditions such as disaster relief and drought, people increasingly need a relatively safe and economical liquid storage container. In this article, we'll cover flexitank storage, also known as truck-mounted flexitank shipping. Fluid bag storage is a relatively new and effective way of storing liquids.
What is a liquid bag?
Flexitank is a soft storage container for bulk materials such as liquids. Depending on the specific gravity of the liquid, they generally have a capacity between 50L and 26 tons. Flexitanks have their own advantages over other types of liquid storage tanks, such as rigid plastic or steel tanks. First, they offer better capacity and weigh less than other storage tanks available. Plus, when they're emptied, they can be folded away to take up little space. Also, they are safe for the environment and the liquids they store.
The characteristics of the liquid bag
The variety of technical fabrics available for the manufacture of flexitanks results in a wide variety of different flexitank categories and sizes. Some flexitanks are temporarily used (such as container flexitanks), while others can hold a liquid for several years at a time, or can be used repeatedly (such as pvc soft water bladders, tpu oil bladders, etc.).
The use of liquid bag
1. Fuel storage
Flexitanks can be used to store liquid fuels such as gasoline, diesel and petroleum. In general, flexitanks are most commonly used by the military or civilians for fuel storage. Rapid access to fuel may be required in emergencies, so flexitanks may be used in field hospitals, emergency airports, or natural disaster relief sites.
2. Drinking water storage
Flexitanks are used in a variety of disaster relief and emergency operations around the world. In the ready state, the flexitank takes up minimal space and can be easily transported to the site for use. Besides fuel, potable water is another fluid that must be readily available. For example, field hospitals, emergency airports, and natural disasters all require potable water storage.
3. Food grade liquid storage
Flexitanks are able to safely and efficiently store food-grade liquid ingredients such as various types of oil, milk, juice, wine, fructose syrup, and more.
4. Storage of Industrial Chemicals
Flexitank is an ideal container for transporting and storing industrial liquid chemicals. These include liquid detergents, lubricants, fertilizers, liquid latex and paints, among others.
5. Disposable and temporary storage
In some applications, liquid storage is only needed temporarily, making purchasing a steel or composite rigid tank not worth the investment. This typically occurs in industrial use or in the event of a sudden drought where liquid storage needs may fluctuate. In this case, the use of flexitanks can reduce overall storage costs. In addition, flexitanks can also be used to transport liquids as they can be packed inside the shipping container for more efficient transport of liquids.
In places such as drought or fire emergency, many people use machine-mounted vehicles to transport water, which makes the safety performance of the modified vehicles worse, and the cost is high, and water is easy to leak during transportation, causing a lot of waste and waste. loss. In order to reduce the cost of phosphorus and lead and increase safety, pvc soft water storage bags came into being.
Features:
The PVC water storage bag is easy to transport, especially suitable for hilly and mountainous areas. The use is less affected by seasonal factors, and it can be folded and stored without trying to reduce the amount of space occupied. The water storage bag has good sealing and corrosion resistance, and has the characteristics of corrosion resistance, acid and alkali resistance.
Instructions:
1. Spread out the water storage bag and put it where it is needed. Be careful not to have sharp things to avoid damage.
2. In order to prevent the water storage bag from rolling, it can be reinforced around the water storage bag when it is placed. It is better that the reinforcement will not scratch or damage the water storage bag.
3. Use a water pump or tap water, connect the water pipe to the water inlet valve of the water storage bag, open the water inlet pipe valve and the exhaust valve switch, and remove the air in the water bag. Start water injection, and after the water bag is full, close the water inlet pipe valve and the exhaust valve.
4. When using a water storage bag, if the bag body is scratched, use a grinding wheel or a wooden file to smooth it out, and apply water to cover it with adhesive tape to repair it. It is best to use the watering repair recommended by the manufacturer.
5. After use, rinse the water storage bag, and after drying, fold it up and place it indoors to avoid sunlight.
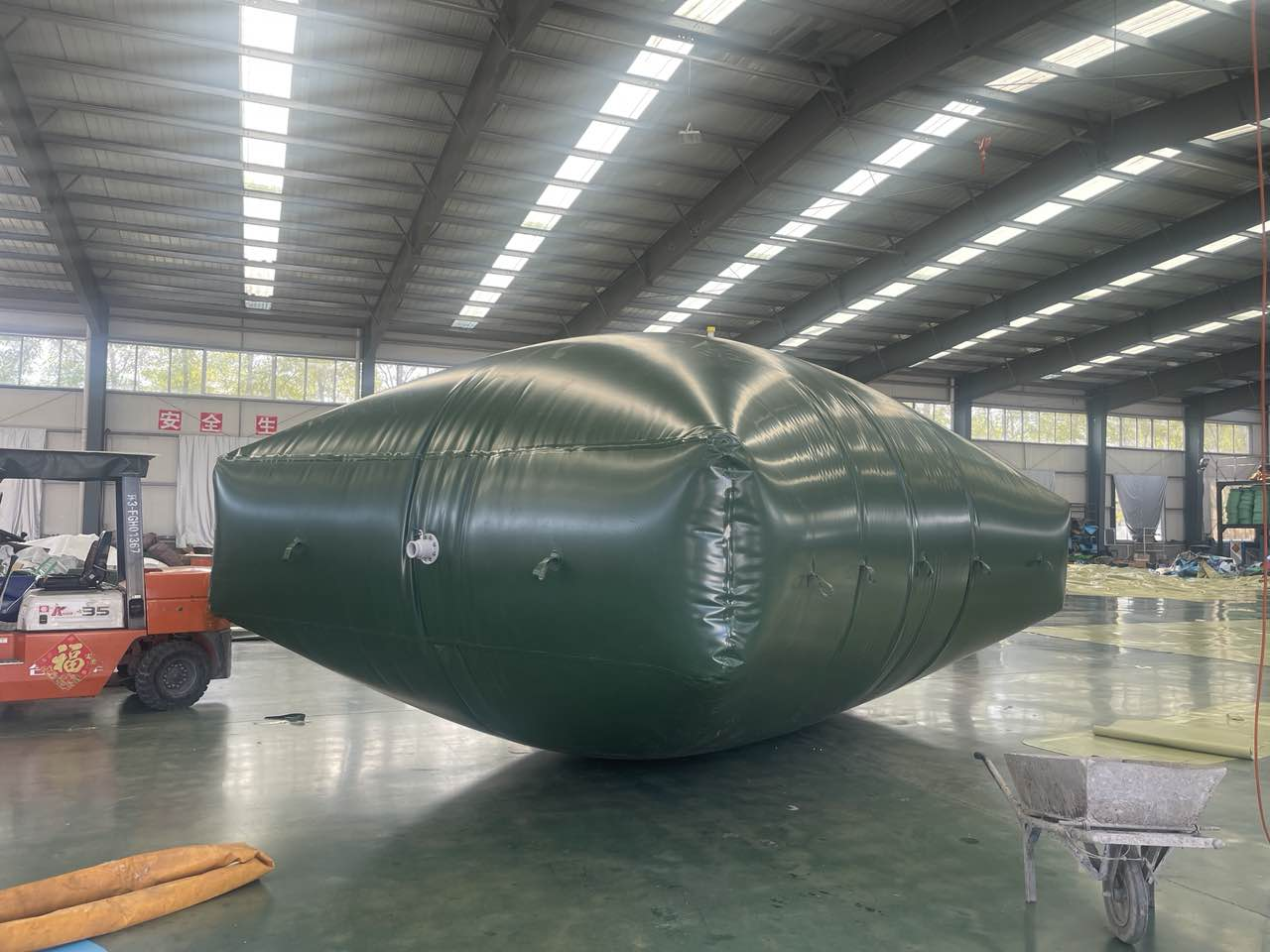

A Water Tank, also known as a Water Bladder or a Water Container, is a portable water storage device that is widely used in camping, hiking, outdoor sports and other occasions. With the popularity of outdoor activities and the increase in people's demand for health and convenience, there are various types of water tanks on the market, and the quality varies. So, how to buy water tanks and find better quality products?
When purchasing a water tank, you should comprehensively consider factors such as material, capacity, design, brand, user evaluation, and price, and choose a product with better quality. In the end, choose a water tank that suits your needs and is reliable in quality, which can provide convenient and comfortable water sources for outdoor activities and daily use, and provide a guarantee for your travel and health protection. Shandong Wolize Biotechnology Co., Ltd. is a professional water tank manufacturer integrating scientific research and development, design, production and sales. Since its establishment, the company has relied on the business philosophy of excellence and customer first, and has attached great importance to the production quality and service quality of products. With the goal of pursuing customer satisfaction, we have won the support and love of our customers. In order to better serve our customers, we provide you with a full range of services from pre-sales to after-sales, and improve our sales service system according to your requirements.






