Aquaculture one-stop solution provider & liquid storage equipment manufacturer.
What Is Recirculating Aquaculture System Definition?
The manufacturing procedures for recirculating aquaculture system definition in Shandong Wolize Biotechnology Co., Ltd. are mostly based on renewable sources. We are acutely aware of our own footprint and the need to concentrate on devising more efficient processes to manufacture this product. And we are increasingly active in the international dialogue on sustainability topics such as climate change. It is also why we are working to understand and manage our impacts both within operations and throughout the product value chain.
Embracing China-made craft and innovation, WOLIZE was founded not only to design products that stimulate and inspire but also to use the design for positive change. The companies we work with express their appreciation all the time. Products under this brand are sold to all parts of the country and a large number are exported to foreign markets.
We are dedicated to providing best-in-class services and outcomes, which can be seen at WOLIZE. Our range of machines give us maximum flexibility and allow us to adapt easily to any size of product series. recirculating aquaculture system definition also can be offered according to the requirements.
Loach is known as "water ginseng". It has high nutritional value and delicious taste, so it is very popular in the market. Loach is a relatively common food, and cultured loaches can often be purchased on the market. Of course, there are many methods of breeding loaches, and there are also various types of breeding ponds, such as earth ponds, rice fields, cement ponds, PE barrels, and plated ponds. Zinc plate canvas pond breeding, etc. How to breed loach? How to build a loach breeding pond?
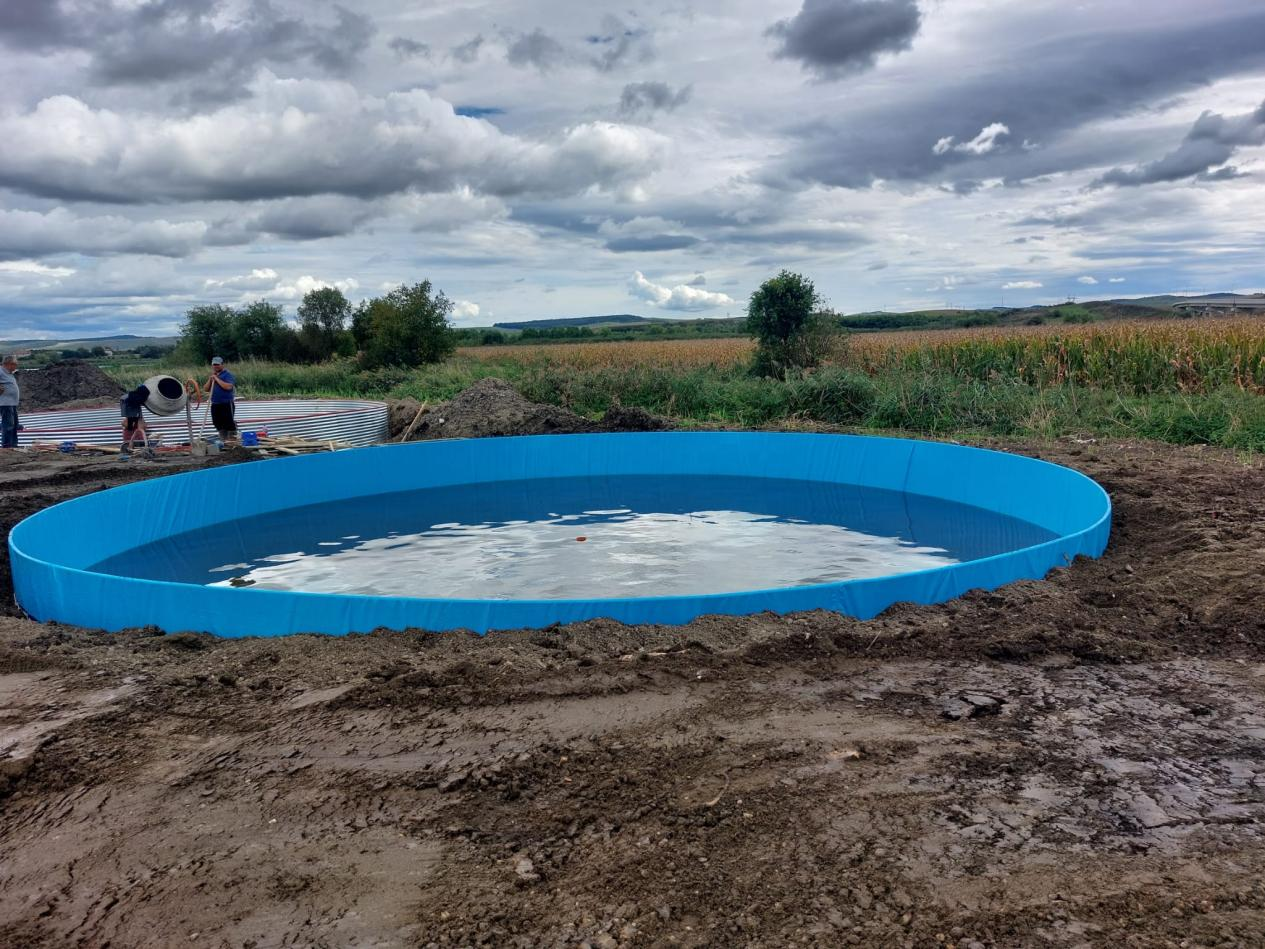

Let’s take the galvanized sheet canvas fish pond, which has been popular in high-density aquaculture equipment in the past two years, as an example. The construction of canvas fish pond is relatively simple. Compared with other ponds such as cement ponds, it is less time-consuming and labor-intensive. It can be installed once it is installed. When put into use, the terrain requirements for breeding sites are not so strict. They can be placed in low-lying mountains, flat rice fields and other places. Although the canvas pool can adapt well to any terrain, the breeding loach should try to choose shelter from the wind and sunny areas, and the terrain is relatively high. And a place with plenty of water. Of course, the water source for aquaculture is the top priority. When raising loach, water quality management must be done well, which can reduce the cost of breeding and increase production.
Galvanized sheet canvas pond farming in deep mountains
When raising loaches, you can plant some aquatic plants such as aquatic plants in the breeding pond, or you can create an aquaponic symbiosis model and plant some vegetables, which can not only clean the water body, but also provide shelter and shelter for the farmed loaches. Provide some microorganisms and small insects for loaches to feed on.
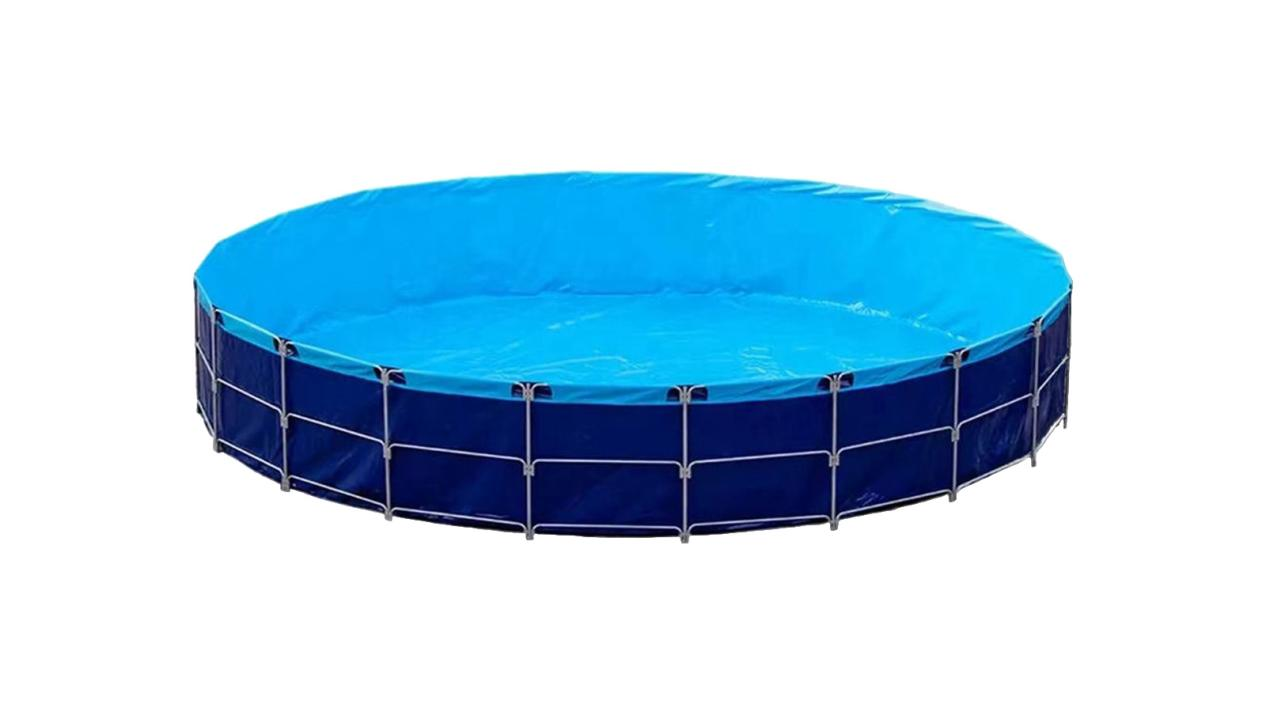

So what should be done about the effluent of wolize's canvas fish pond? The materials needed to prepare for the sewage of the canvas pond are roughly matching fish toilets, a number of sewage drainage pipes (PVC water pipes and air pipes), and the entire drainage and sewage system has water sources, inlet and outlet, various channels, sluice gates, catchment pools, and so on. In order to facilitate sewage discharge, the bottom of the fish pond is generally recommended to make the bottom of the pot shape, so that some of the waste and slag of the flowing fish pond through the water body will converge to the center of the fish pond, in this position to install the fish toilet, the fish pond excrement can be smoothly discharged through the fish toilet and pipe, to keep the water quality clean.
The sewage design of the canvas fish pond is relatively simple, because the canvas fish pond is a regular shape, there is no cleaning dead corners, there will be no silt blockage, and the installation location of the fish toilet and pipeline can be determined according to the site selection and personal needs of the fish pond, and the limitation is relatively small. In addition to fish toilet sewage, conditions can also be made into fish and vegetables symbiotic circulating water filtration system, fish and vegetables double harvest saving resources is more ecological and environmental protection.
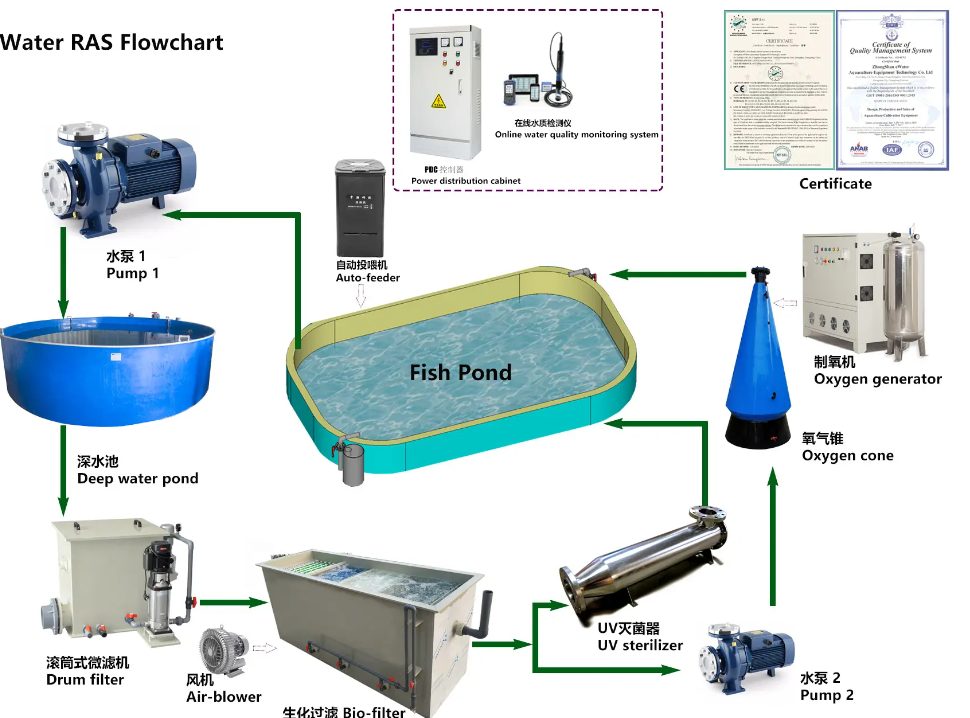
Recirculating Aquaculture System (RAS) circulating water technology is a technology that can change aquaculture in open water bodies into controlled environment farming. This technology can continuously renew the water body and has unique technical advantages. When using RAS technology to breed aquatic products, it is necessary to start from the hydrological conditions of the breeding site and make different adaptive designs in each link of the system.
First of all, circulating water technology can turn the uncontrollable breeding environment into controllable, basically eliminating the influence of external factors (such as harmful bacteria, viruses, pesticide residues in the soil, excessive heavy metals, etc.) on organisms. In the process of recirculating aquaculture, not only do not need to add any antibiotics, but also add various beneficial bacteria to help the fish intestines restore health, so that the produced aquatic products are truly healthier and pollution-free.
Secondly, the circulating water plant is different from the traditional soil pond culture, it can be built on any land for agricultural facilities or industrial land. Circulating water plants can be built around super cities, such as Chongming Island in Shanghai, Shenshan Cooperation Zone in Shenzhen, and Development Zone in Chengdu. Therefore, circulating water technology can to a certain extent solve the problems of loss, cold chain, and water truck logistics costs caused by the logistics and transportation of production and sales during aquaculture. However, considering the actual cost of water for aquaculture, the factory needs to be located in an area close enough to the water source to optimize the cost structure.
Finally, recirculating aquaculture technology can meet the needs of agricultural orders, and can plan production in advance according to species and quantity. In the production process, it is possible to use AI image recognition (to assist in the inventory of biological assets), automatic feeding machines (to save labor costs), and automatic fish screening/separation devices (to reduce external disturbance of biological growth and reduce mortality), which has the advantages of Many advantages. For fresh food e-commerce companies such as Hema and Dingdong, the quality control of aquatic products has always been their biggest pain point, and the circulating water technology is exactly what makes the production process fully transparent, real-time inventory, and predictive breeding The cycle can help downstream fresh food e-commerce companies to provide consumers with a stable and healthy supply of goods.
A Recirculating Aquaculture System (RAS) is a closed-loop system designed to provide a controlled environment for fish farming. Unlike traditional open systems, RAS continuously purifies and reuses water, significantly reducing waste and minimizing the environmental footprint. This system consists of several components that ensure water and nutrient recycling, making it a highly efficient and sustainable solution.
- Water Recycling: The system water is purified and reused, eliminating the need for additional freshwater and reducing the demand for wastewater treatment.
- Nutrient Recycling: Biological filters break down ammonia and other nitrogenous waste products, reducing the load on the environment.
- Energy Efficiency: The system requires minimal energy input due to water and nutrient recycling, making it highly energy-efficient.
Advantages of RAS for Sale Over Traditional Waste Management Options
Reduced Environmental Impact
RAS systems minimize the strain on natural resources. Traditional methods often lead to water pollution, methane emissions, and the generation of landfills. RAS systems eliminate waste through recycling, making them a greener and more sustainable alternative.
Cost-Effective
RAS systems are cost-effective in the long run due to their ability to reuse water and reduce the need for additional infrastructure. This makes them a viable option for both small-scale and large-scale operations.
No Landfill Dependency
Traditional waste management often involves landfills, which can contribute to environmental degradation. RAS systems do not require landfills, as they recycle water and nutrients, reducing pollution and waste disposal issues.
Eco-Friendly and Reliable
RAS systems are environmentally friendly and reliable, making them an excellent choice for sustainable agriculture and aquaculture. They are also highly adaptable, suitable for various waste types and locations.
RAS for Sale in Action
Real-world implementations of RAS for sale have demonstrated its effectiveness in reducing waste and conserving resources. For example:
- Aquaponics Farms: Many aquaponics farms use RAS to combine fish farming and hydroponic plant growth. This approach eliminates the need for separate water sources for fish and plants, reducing water waste and energy consumption.
The Future of RAS for Sale
As sustainability becomes a priority, the demand for innovative waste management solutions like RAS is expected to grow. With advancements in technology, RAS systems can become even more efficient and scalable. For example:
- Modular Design: RAS systems can be designed in a modular fashion, allowing them to be adapted to different geographic locations and waste types.
- Integration with Renewable Energy: RAS systems can be integrated with renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, to further reduce their energy footprint.
Adapting RAS for Sale to Different Needs
RAS systems are highly customizable, making them suitable for a wide range of waste management needs. Whether you are dealing with organic waste, agricultural runoff, or electronic waste, RAS can be adapted to meet your specific requirements. For example:
- Electronic Waste Recycling: RAS systems can be equipped with specialized filters to process electronic waste, separating metals, plastics, and other materials for recycling.
- Waste-to-Energy: RAS systems can also be used in waste-to-energy processes, where they help convert waste materials into usable energy.
Embracing a Sustainable Future
The Recirculating Aquaculture System for Sale represents a significant advancement in sustainable waste management. Unlike traditional methods, RAS systems offer a reliable, efficient, and eco-friendly solution for both aquaculture and waste recycling. By reducing water and nutrient usage, minimizing environmental impact, and creating a closed-loop system, RAS for sale provides a sustainable alternative to conventional waste management.
As the world continues to face environmental challenges, its crucial that we adopt innovative solutions like RAS. Whether you are an aquaculture business, a municipality, or an individual looking to reduce your environmental footprint, RAS for sale offers a promising and innovative solution. Lets work together to create a sustainable future!
The materials used in aquaculture systems are crucial to reducing environmental impact. Manufacturers are increasingly focusing on recycled and biodegradable materials to minimize waste and promote environmental health. For instance, consider the case of EcoFiber Aquatic Solutions, which developed biodegradable pond linings that have significantly reduced waste in their clients' operations. These materials not only reduce the environmental footprint but also offer innovative solutions for improving water management and feed efficiency.
Advanced materials, such as nanomaterials and bio-based composites, are also being developed. For example, Nanotech Innovations has created a nanomaterial that enhances the durability and biodegradability of pond liners, reducing both waste and environmental impact. These advancements are transforming traditional aquaculture materials and making them more sustainable.
Enhancing Water Quality in Aquaculture Systems
Maintaining optimal water quality is vital in aquaculture, as it directly impacts the health and productivity of the fish. Think of water quality as the lifeblood of a garden or a precious gemcritical to its health and beauty. Manufacturers are investing in both biological and chemical solutions to achieve this.
Biological treatments, such as those involving natural microorganisms, are used to improve water health without harming the environment. Imagine a garden where beneficial insects and plants help ward off pests naturally. Similarly, water treatment bacteria are used in aquaculture to maintain water quality. Chemical and mechanical solutions, including advanced water treatment chemicals and filtration systems, are also being developed. For example, AquaTech Filters have introduced a mechanical filtration system that reduces the need for chemical inputs while maintaining clean and healthy water.
Biotechnology in Sustainable Aquaculture Systems
Biotechnology is playing a significant role in advancing sustainable aquaculture. Genetic improvements, such as the development of disease-resistant fish varieties, are enhancing productivity and resilience. For instance, AquaGenetics has created disease-resistant tilapia strains that significantly reduce the need for antibiotics, promoting healthier fish and more sustainable farming practices.
Additionally, biotechnology is being applied to innovations in feed development, disease control, and waste management. One notable example is GenBio Feed, which has developed a feed formula that reduces waste and improves digestibility, effectively optimizing resource use and reducing environmental impact.
The Role of the Supply Chain in Sustainable Aquaculture Systems
The supply chain is a critical component of sustainable aquaculture. Manufacturers are working to ensure that the inputs used, such as feed, water, and other materials, are sourced sustainably. Closed-loop systems, which recapture and reuse resources, are being developed to minimize waste and reduce resource consumption. For example, RecycleMelt Systems have implemented closed-loop recycling systems that recycle water, feed, and waste materials, significantly reducing their environmental footprint.
Step-by-Step Explanation of Closed-Loop Systems
A closed-loop system works by capturing and reusing water and nutrients. The process starts with a water treatment system that purifies and recirculates water. Next, advanced feed systems ensure that the nutrients are efficiently distributed, reducing waste. Waste materials are collected and processed into organic fertilizers, completing the cycle. This process not only reduces waste but also enhances the sustainability of the entire aquaculture system.
Case Studies of Manufacturers Leading Sustainable Aquaculture Systems
Several case studies highlight manufacturers' contributions and the tangible benefits of their innovations. For instance, EcoFiber Aquatic Solutions biodegradable pond linings have reduced waste by up to 50% in many operations, making a significant environmental impact.
Similarly, Aquatic Filter Systems advanced water filtration systems have helped fish farms reduce chemical inputs by 30%, leading to healthier fish and more sustainable practices. These innovations have been adopted by many aquaculture operators, leading to positive market responses and enhanced sustainability.
The Future of Sustainable Aquaculture Systems and Manufacturers
The future of sustainable aquaculture is promising, with emerging trends such as vertical farming and aquaponics offering new opportunities. Manufacturers are at the forefront of driving these innovations by providing sustainable technologies and materials. For example, AquaVert has developed a vertical farming system that uses 90% less water than traditional methods, reducing resource consumption and promoting sustainability.
By staying invested in research and development, manufacturers can play a key role in shaping the future of aquaculture. Collaborations with governments, researchers, and other stakeholders will be essential to overcoming challenges and ensuring the industrys long-term success.
To Recap
In essence, manufacturers are driving the sustainable development of aquaculture systems through innovation, material selection, water quality management, and efficient supply chains. Their contributions are crucial for creating systems that are both efficient and environmentally friendly. By continuing to innovate and invest in sustainable practices, manufacturers can ensure that aquaculture remains a vital and eco-friendly component of global food production.
Thank you for reading. By embracing sustainable methods and technologies, manufacturers are leading the way in creating a more resilient and environmentally friendly aquaculture industry.
Recirculating Aquaculture Systems (RAS) are revolutionizing the aquaculture industry by employing a highly efficient water recycling method. Unlike traditional systems that discard water and rely on lake or pond water, RAS recycles water, significantly reducing water and energy consumption. This efficiency not only lowers costs but also enhances sustainability. Understanding the prices of RAS is crucial for businesses and consumers to assess the cost-effectiveness of producing fish and other aquatic organisms.
Factors Influencing RAS Prices
The price of RAS is influenced by several key factors. These include supply and demand dynamics, technological advancements, regulatory environments, and market saturation. Additionally, environmental regulations and sustainability practices play a significant role in shaping RAS prices.
Cost Efficiencies and Technological Advancements
Advanced RAS systems can save up to 90% of water usage compared to traditional pond-based methods. This efficiency translates into lower operational costs. Technological advancements such as high-efficiency filtration systems and improved monitoring technologies are driving down costs and enhancing system efficiency. For example, a study by the Pacific Institute highlights the substantial water savings and cost reductions associated with RAS.
RAS Prices for Specific Fish Species
Various fish species are commonly farmed using RAS, including tilapia, anchovies, and farmed grouper. The pricing of these species varies based on market demand, supply availability, and system efficiency:
- Tilapia: Tilapia is one of the most economically significant fish species farmed in RAS globally. Its high demand and relatively low production costs make it a popular choice. Prices for tilapia in RAS systems typically range from $2 to $3 per kilogram, reflecting its market advantage.
- Anchovies: Anchovies are another common RAS species, with prices ranging from $4 to $6 per kilogram. Higher production costs due to their sensitivity to water quality make them slightly more expensive.
- Farmed Groupers: Farmed groupers are known for their premium prices, with prices ranging from $10 to $20 per kilogram in RAS systems. Their higher demand and production costs justify these premium prices.
Comparing RAS Prices to Conventional Methods
Traditional aquaculture methods often rely on lake or pond water, which can be more expensive and less efficient compared to RAS. RASs ability to recycle water and energy makes it a more cost-effective and sustainable option. For instance, a study by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) found that RAS can save up to 90% of water usage and 75% of energy compared to traditional pond-based systems.
Future Trends in RAS Prices
Technological advancements in RAS systems are expected to further reduce costs and improve efficiency. For example, the development of more energy-efficient filtration systems and advanced monitoring technologies can significantly lower operational costs. Global market dynamics, such as trade policies and environmental regulations, will continue to impact RAS prices. Additionally, the focus on sustainability and scalability will remain key factors in shaping the future of RAS pricing.
Conclusion
In conclusion, businesses and policymakers should consider adopting RAS as a strategic approach to enhance both cost-effectiveness and sustainability. By investing in efficient technologies and remaining adaptable, companies can stay ahead of the curve. Educating the public about the benefits of RAS can also drive wider adoption. Future research should explore the long-term environmental and economic impacts of RAS pricing trends. By embracing RAS, the aquaculture industry can achieve greater sustainability and efficiency, contributing to a healthier planet.





